Improving the validity of brain-behavior associations
Stanford University
What does a brain-behavior association mean?
What does a brain-behavior association mean?

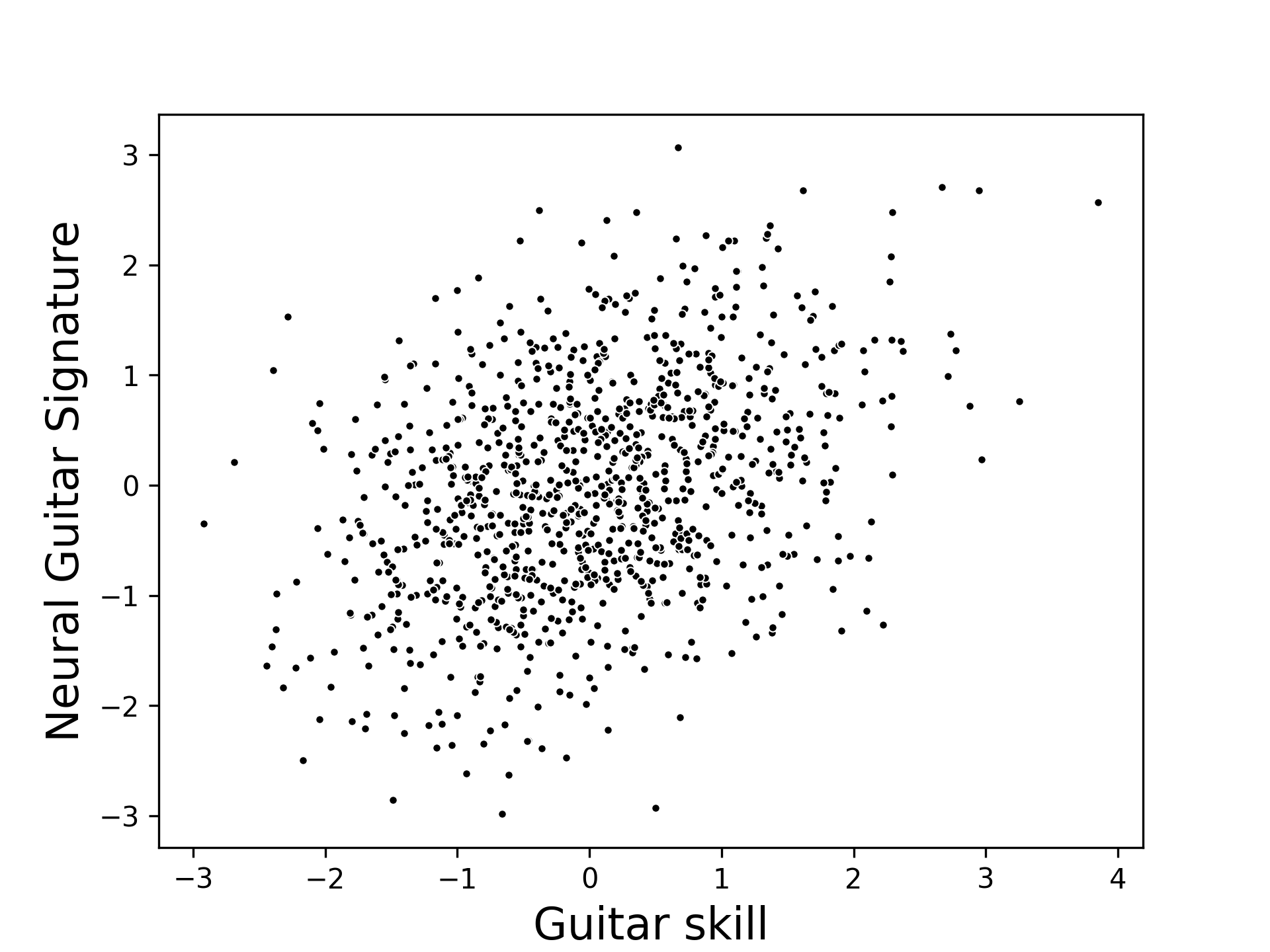
What does a brain-behavior association mean?



What does a brain-behavior association mean?




What does a brain-behavior association mean?







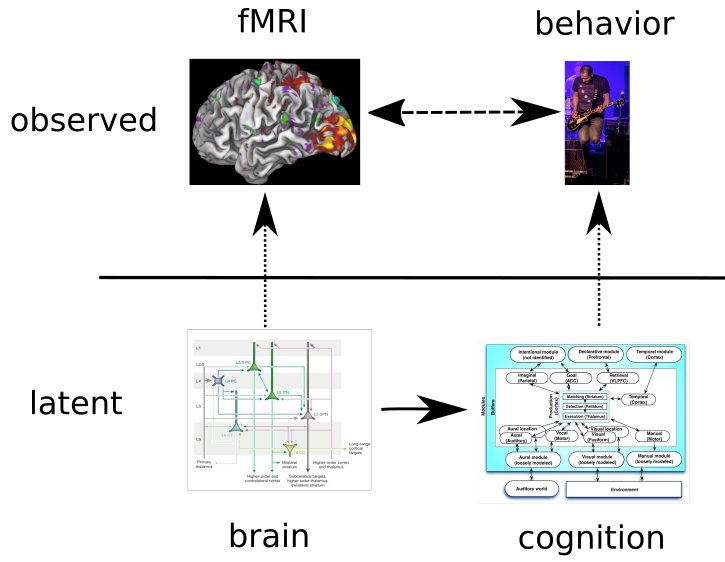
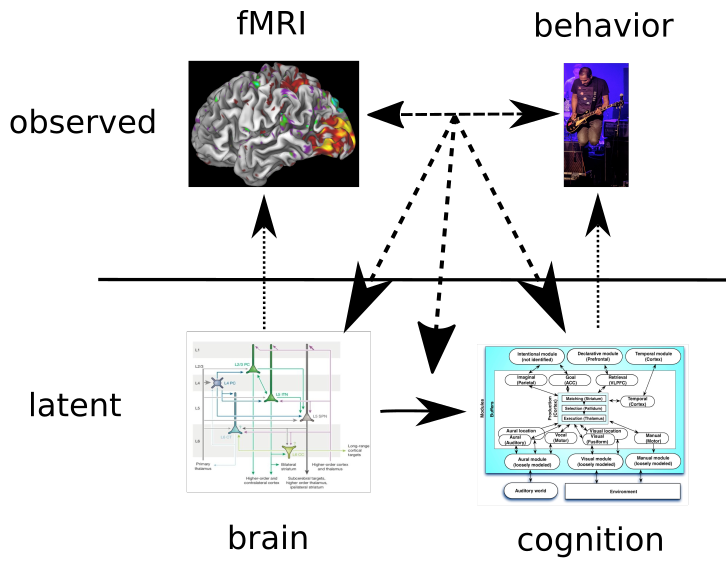
Assuming this model is true, what kinds of neural differences could give rise to cognitive differences?
“Brain efficiency”
“A series of investigations in normal subjects indicate an inverse relationship between brain glucose metabolic rate and psychometric measures of intelligence. . .These studies have been interpreted as evidence for a brain efficiency model of intelligence: Intelligence is not a function of how hard the brain works but rather how efficiently it works.” (Haier et al., 1992)
“Brain efficiency”
“A series of investigations in normal subjects indicate an inverse relationship between brain glucose metabolic rate and psychometric measures of intelligence. . .These studies have been interpreted as evidence for a brain efficiency model of intelligence: Intelligence is not a function of how hard the brain works but rather how efficiently it works.” (Haier et al., 1992)”
Is this really an explanation?
Efficiency: A thought experiment
- A Prius and a Porsche both drive from San Francisco to Los Angeles via the same route at the same speed.
- The Prius uses half as much fuel as the Porsche. How do we explain this?

Efficiency: A thought experiment
- The Prius has a gas-electric hybrid engine (which uses surplus engine power to generate electricity which is then turned back into drive power) and regenerative braking (which captures energy that would otherwise be lost as heat).
Poldrack, 2015
Efficiency: A thought experiment
- The Prius has a gas-electric hybrid engine (which uses surplus engine power to generate electricity which is then turned back into drive power) and regenerative braking (which captures energy that would otherwise be lost as heat).
- The Prius is more efficient.
Poldrack, 2015
Explaining brain-behavior associations
- “Efficiency” is a non-explanation
- It simply renames the phenomenon
- What kinds of neural differences might actually explain these associations?
- Different intensity of neuronal activity
- Different duration of neuronal activity
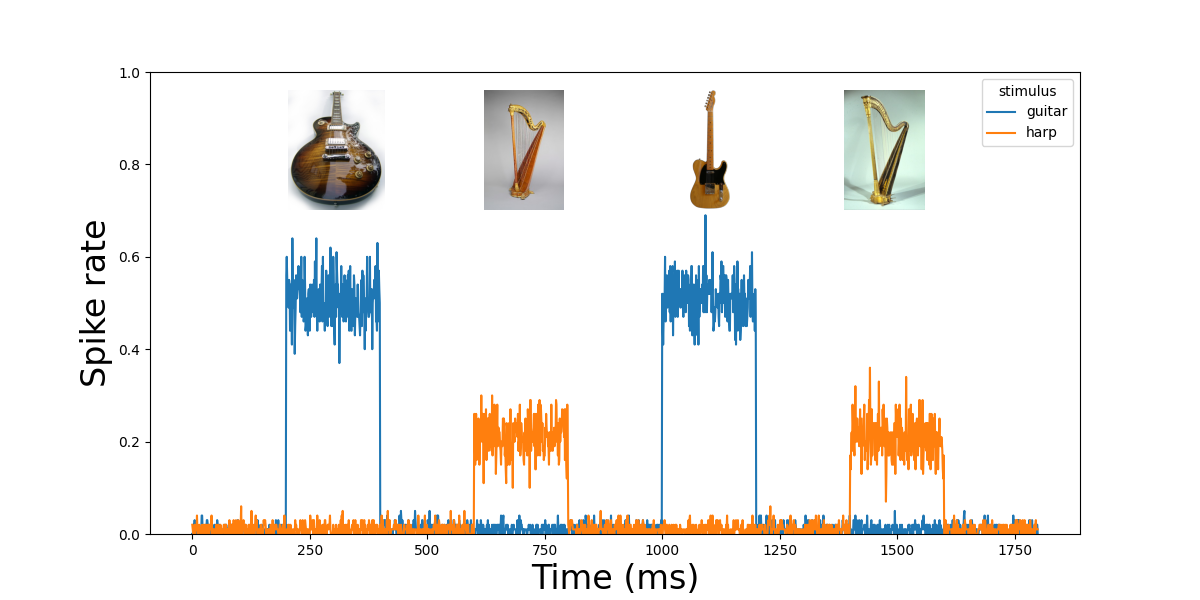

Difference in intensity of neural activity

Difference in duration of neural activity
Changes in rate vs. duration of neural firing are indistinguishable in fMRI
Same duration, different amplitude
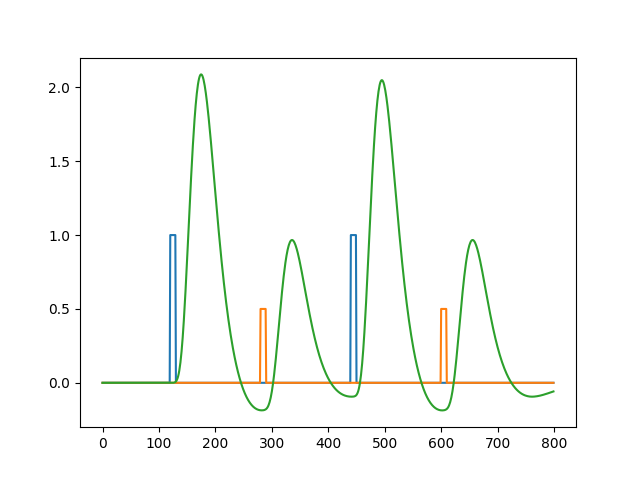
Same amplitude, different duration
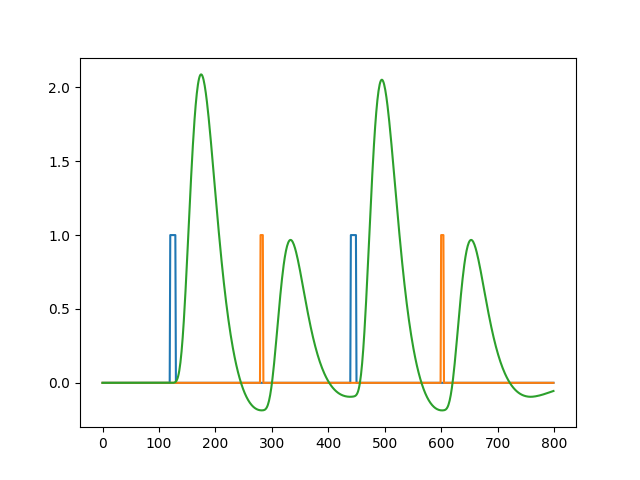
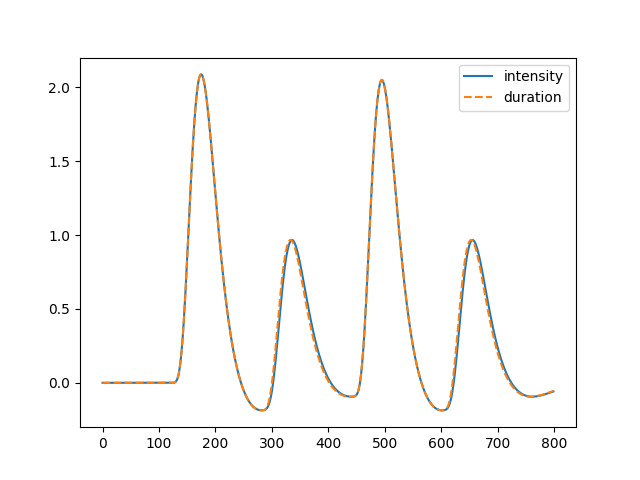
The effects of amplitude and duration are indistinguishable in the fMRI signal
The response time paradox
- In cognitive psychology, differences in RT are the measure of interest
- Thus, nearly all task comparisons will exhibit a difference in RT
Mumford et al, 2023
The response time paradox
- From the standpoint of fMRI, these same RT differences reflect a potential confound
- We can’t tell whether the differences in activation are truly due to differences in neural computation, or simply due to a “time on task” confound
- Known since Grinband et al. (2008)
Mumford et al, 2023

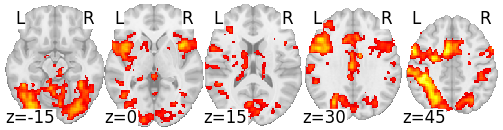
Response time correlates in fMRI are very strong
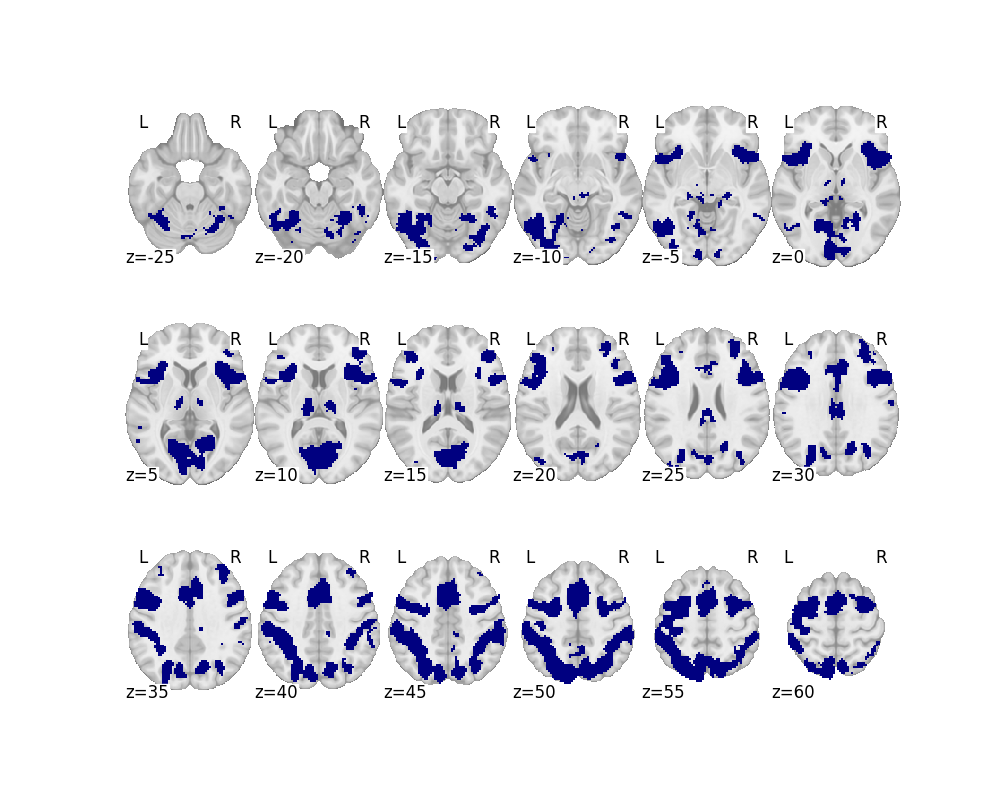
Conjunction across 7 tasks
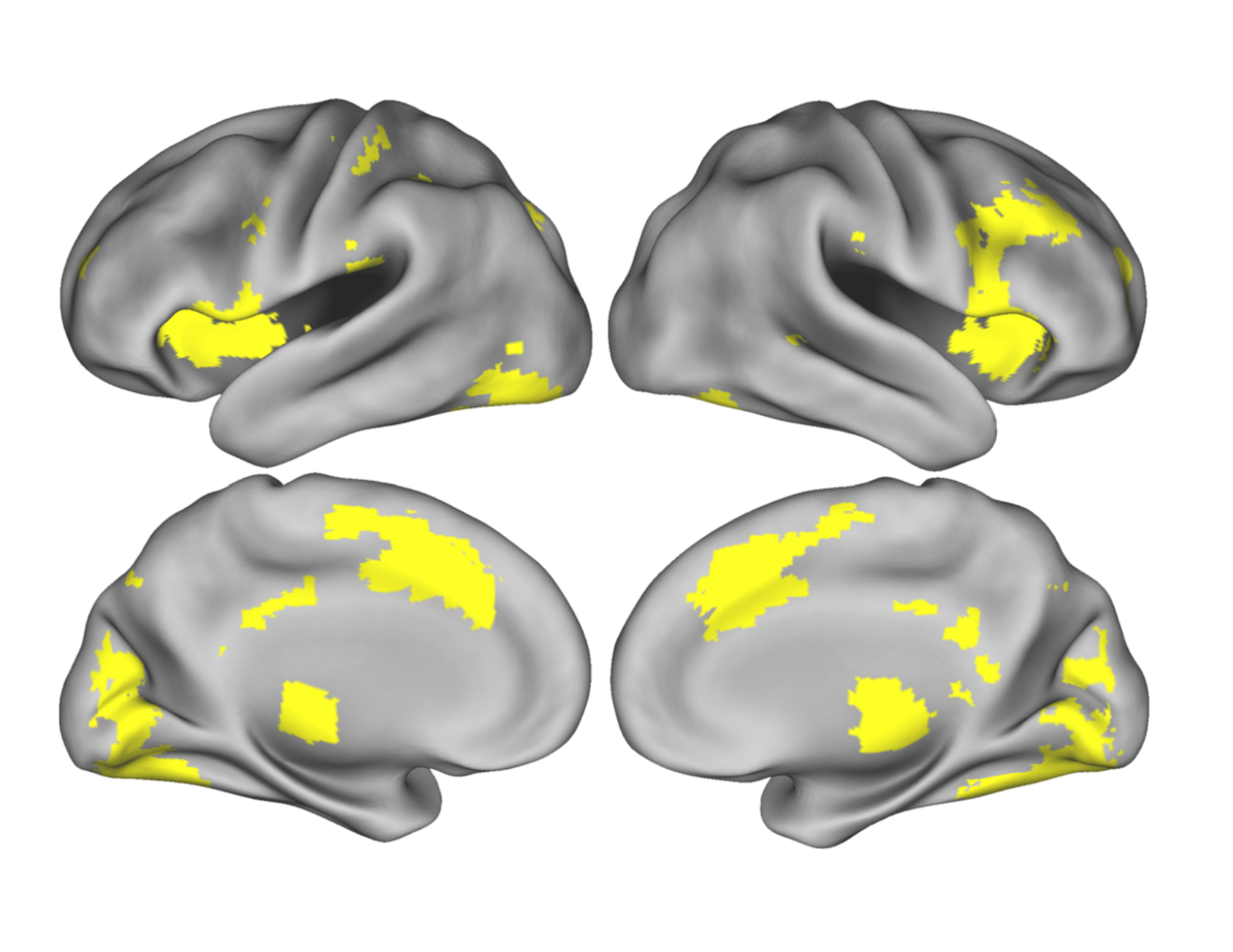
Conjunction across 4 tasks
Yarkoni et al., 2009
Mumford et al, 2023
What about brain-behavior associations?
- Under the standard analysis approach (ignoring RT), if there are:
- differences in the overall BOLD response (regardless of condition) across people
- variability in the RT difference between conditions across people
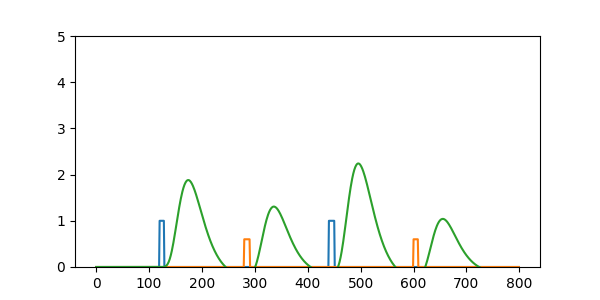

What about brain-behavior associations?
- Under the standard analysis approach (ignoring RT), if there are:
- differences in the overall BOLD response (regardless of condition) across people
- variability in the RT difference between conditions across people
- This can induce an artifactual correlation between activation (between-condition comparisons) and the RT difference.
- Even if the average RT difference between conditions is zero across subjects!
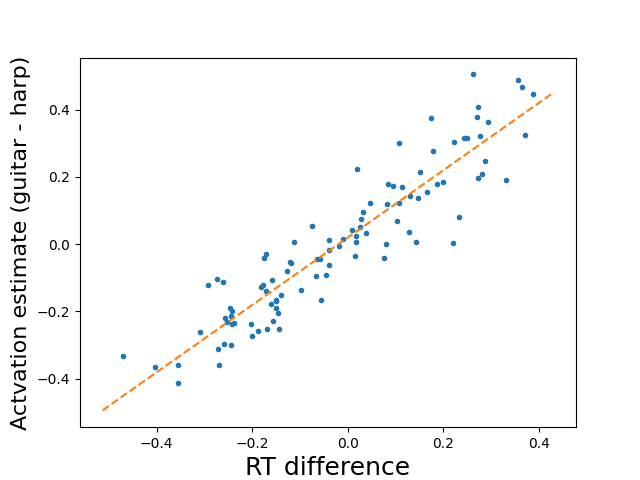
Mumford et al, 2023
Spurious brain-behavior correlations
- When overall BOLD response (across all conditions) differs by some subject feature (e.g. age), then this can lead to spurious brain-behavior associations with that feature
- Even when there is no true relationship between age and activation (condition differences) or RT!

Mumford et al, 2023
Can it be fixed by regressing out RT at the group level?
- No!
- Simulations show that regressing RT out at the group level could actually increase the size of the spurious effect.
Without RT regressor in group model:
| t | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 2.698 | 0.008 |
With RT regressor in group model:
| t | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 7.163 | 0.000 |
Mumford et al, 2023
Solution: Model RT at the first level
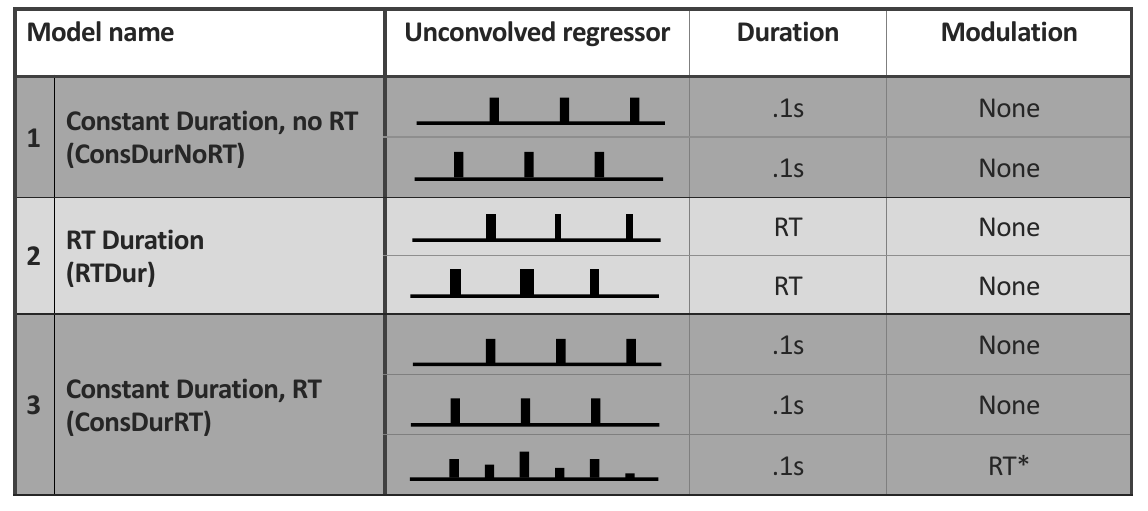
←
The standard model
←
The Grinband et al. (2008) model
←
The Mumford et al. model
The Constant Duration + RT model allows quantification of the unique contributions of time on task and condition differences
Mumford et al, 2023
Are we throwing out the baby with the bathwater?
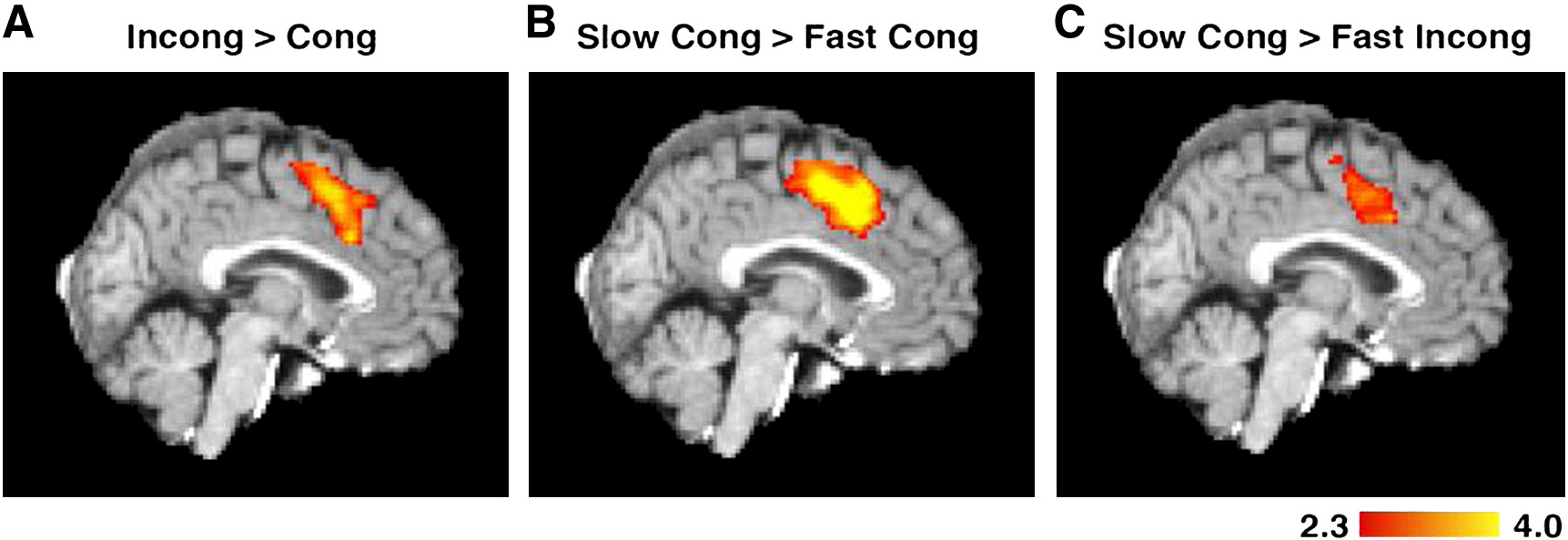
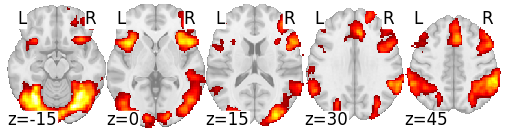
Activation for Stroop effect disappears after removing RT effect
Grinband et al., 2011 (N = 23)
With sufficient power, we can (sometimes) find specific effects after removing RT
Without RT modeling
Stroop
(inc - con)
With RT modeling
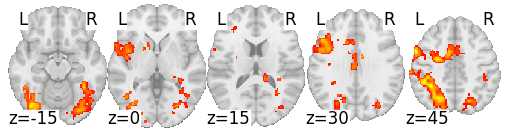
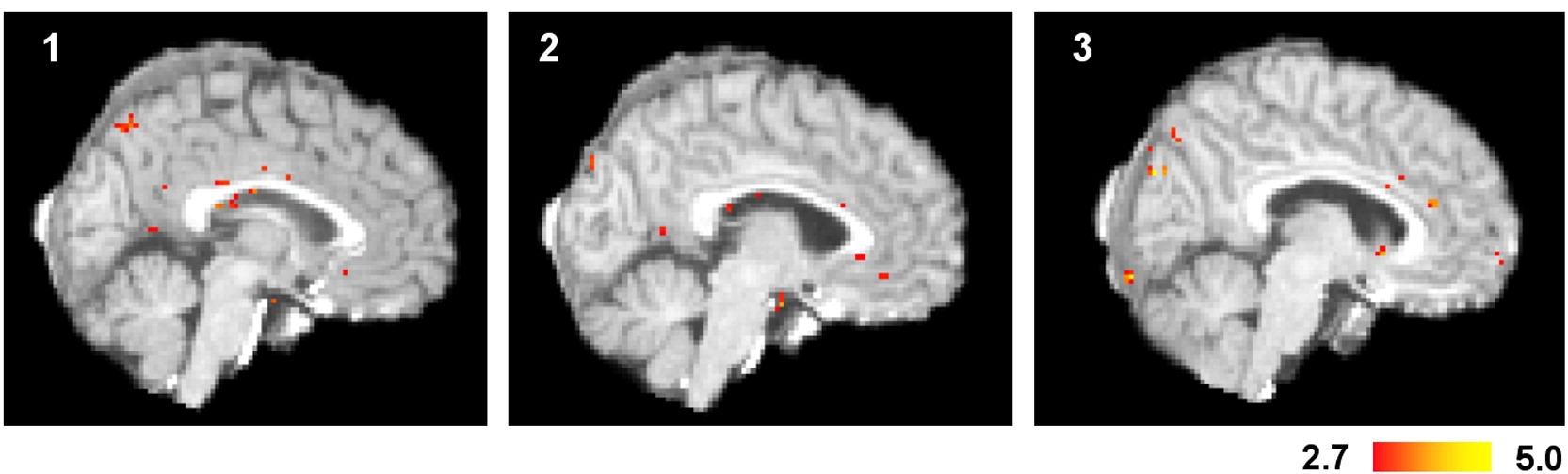
With sufficient power, we can (sometimes) find specific effects after removing RT
Without RT modeling

Stroop
(inc - con)
With RT modeling

Task switching
(TS - CS)
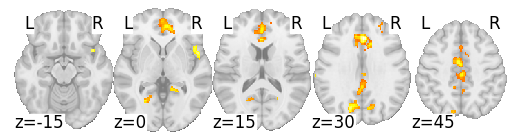
With sufficient power, we can (sometimes) find specific effects after removing RT
Without RT modeling

Stroop
(inc - con)
With RT modeling

Task switching
(TS - CS)


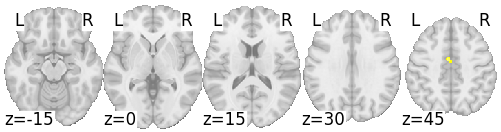
Stop signal
(FS - go)
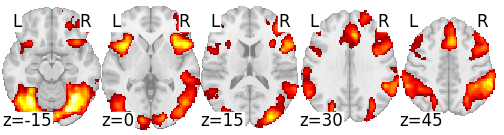
Bissett et al., unpublished
Modeling RT at the first level prevents suprious relations with RT and other correlates of BOLD response
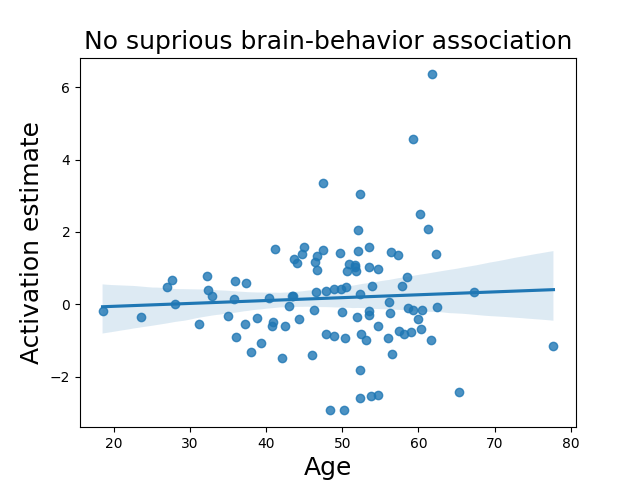
Without first-level RT modeling:
| t | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 2.698 | 0.008 |
With first-level RT modeling:
| t | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.562 | 0.575 |
Mumford et al, 2023
Confound modeling is not a magic balm
- There is a general sense evident from brain-behavior association studies that regression can magically cure all that ails us
- Simply adding regressors will not fix many problems, and can cause others
- Collider bias
- When a confound regressor is a common effect of X and Y variables
- Measurement error (Westfall & Yarkoni, 2016)
- When confound variables are measured with error, including them can inflate error rates (sometimes to nearly 100%)
- Collider bias
- We need a greater focus on causal justification for our statistical models (Wysocki et al., 2022; Kopal et al., 2023)

Conclusions
- Response time is a major potential confound for all task fMRI studies
- Without adjustment, it is impossible to determine whether activations simply reflect time on task
- If response time effects are not modeled at the first level, they can result in sprious brain-behavior associations
- This poses a major problem for large projects that share statistical results from first-level models that do not include RT
Acknowledgments
The Poldrack Lab


Jeanette Mumford



Funding
https://poldrack.github.io/talks-BrainBehaviorAssociation/